Mastering Microbiology: A Comprehensive Guide for Medical Students14 min read
Introduction to Microbiology: The Importance for Medical Students
Table of Contents
Microbiology is a crucial subject for medical students as it provides a foundation for understanding infectious diseases and their management. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive study guide for medical students, covering various aspects of microbiology that are essential for clinical practice.
Microbiology 101: Understanding the Fundamentals
Before diving into the details, it is important to grasp the fundamental concepts of microbiology. This section will cover the basics of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, as well as their structure, classification, and growth requirements.
Essential Microbiology Textbooks and Study Materials
Having reliable study materials is crucial for mastering microbiology. In this section, we will explore some highly recommended textbooks and study resources that cover the key topics in microbiology. These resources will help students gain a comprehensive understanding of the subject and prepare for exams.
- First Aid
- Kaplan Microbiology
- Toronto Notes
- Becker Series
Microbiology Online Resources: Websites, Videos, and More
In addition to textbooks, online resources can greatly enhance the learning experience. This section will provide a list of reputable websites, educational videos, and interactive tools that offer valuable microbiology resources. These online resources can be accessed anytime and anywhere, making them convenient for self-study and review.
Paid Resources:
- Sketchy Micro
- Brain Scape (Free Flash Cards)
- Board & Beyond
- Osmosis
- USMLE RX
Free Resources:
2024 Sketchy Micro [How to get it for free]
Personally, I’ve found that Sketchy Micro is the best resource to study microbiology. Each video is a masterpiece – microbiology has changed from the hardest subject, where studying it was a pain in the neck, to a fun experience. A lot of work has been done to provide the best mnemonics for easy study.
I know for some people it’s a big investment, but I’m sure it deserves every penny. You can access Sketchy Micro and get a free trial through this link.
If you’re living in banned countries where you can’t pay for Sketchy, you can access study material through Telegram channels or websites. It won’t give you the latest videos or additional files, but it can still be helpful.
Mastering Microbiology Terminology: Key Definitions to Know
The secret language of the lab coat crowd. Don’t let all those ten-dollar words intimidate you, my fellow future micro mavens.
With the right tools and strategies, you can become fluent in no time.
First up, get cozy with resources like Sketchy Micro and Osmosis – their visual aids and mnemonic devices will have you memorizing terms like “capsid” and “endospore” faster than you can say “Escherichia coli.”
And don’t forget to supplement that with good old-fashioned flashcards, whether it’s the classic pen-and-paper version or the spaced repetition magic of Anki.
Trust me, taking the time to really understand definitions like “virulence factor” and “quorum sensing” will pay off big-time when you’re diagnosing infections and prescribing treatments.
After all, you can’t be an expert microbiologist without mastering the lingo.
So dive in, get those terms down pat, and watch your knowledge – and confidence – skyrocket.
Before you know it, you’ll be throwing around “endotoxin” and “exotoxin” like a pro. Microbiological success awaits!
High-Yield Microbiology Topics for Medical Exams
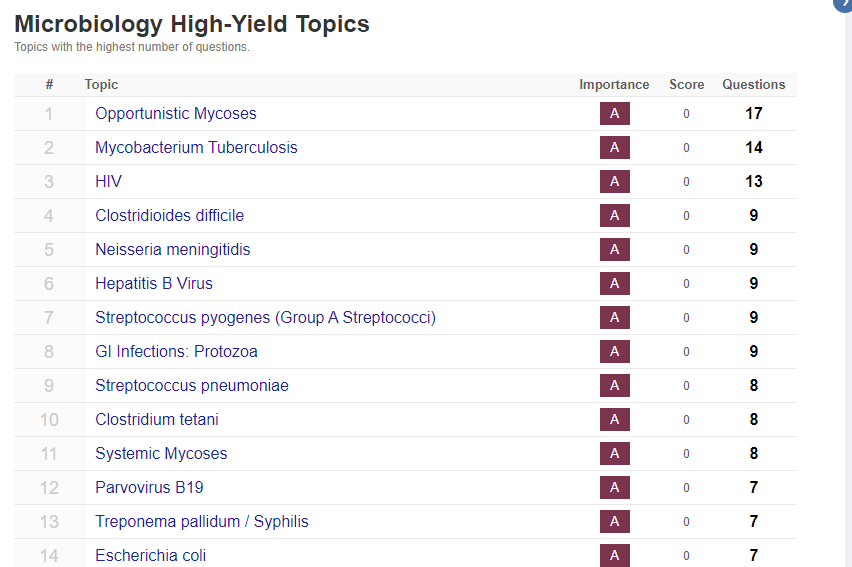
Medical exams, such as the USMLE, often include microbiology questions that require a solid understanding of high-yield topics. This section will identify the most important microbiology topics that students should focus on during their exam preparation. By prioritizing these topics, students can maximize their chances of success in the exams.
- Bacterial cell structure and function
- Bacterial genetics and mechanisms of antibiotic resistance
- Viral structure, classification, and replication
- Innate and adaptive immune responses
- Pathogenesis of bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic infections
- Epidemiology and transmission of infectious diseases
- Diagnosis of infectious diseases (microscopy, culture, serology, molecular techniques)
- Antimicrobial agents and mechanisms of action
- Gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria (e.g., Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Escherichia, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas)
- Mycobacteria and atypical mycobacteria (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium leprae)
- Anaerobic bacteria (e.g., Clostridium, Bacteroides)
- Medically important fungi (e.g., Candida, Aspergillus, Cryptococcus)
- Medically important parasites (e.g., Plasmodium, Giardia, Toxoplasma, Trypanosoma)
- Viral pathogens (e.g., HIV, hepatitis viruses, influenza viruses, herpesviruses)
- Mechanisms of microbial pathogenesis (e.g., toxins, adhesins, invasins)
- Host-microbe interactions and the human microbiome
- Infection control and prevention (e.g., sterilization, disinfection, hand hygiene)
- Vaccines and their mechanisms of action
- Emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases
- Zoonotic infections and their epidemiology
- Remember, this list is not exhaustive, and the specific topics and their depth may vary depending on the USMLE Step 1 exam’s focus and updates. It’s essential to review the latest USMLE content outline and study materials to ensure you cover all the relevant topics.
Developing Effective Microbiology Study Strategies
Studying microbiology effectively requires a well-planned strategy. This section will provide tips and techniques for developing effective study strategies specifically tailored to microbiology.
Break down the subject into manageable topics (e.g., bacterial structure, viral replication, immune responses, disease pathogenesis)
- Create a balanced study plan to understand core concepts and memorize key details
- Actively engage with the material by creating visual aids (diagrams, flowcharts, mnemonics) to strengthen recall
- Practice regularly with practice questions and case studies to apply your knowledge
- Supplement textbook learning with research papers, review articles, and online resources
- Participate in study groups or peer-to-peer discussions to reinforce understanding and gain new perspectives
- Regularly assess your progress and adjust your strategies as needed
- Prioritize your physical and mental well-being (sleep, exercise, breaks) to optimize learning and retention
- Adopt a strategic and holistic approach to develop a strong foundation in microbiology for the USMLE Step 1 exam
Microbiology Case Studies: Enhancing Clinical Reasoning Skills
Case studies are invaluable tools for applying microbiology knowledge to real-life clinical scenarios.
Engaging with microbiology case studies is a powerful way to develop your clinical reasoning skills. These case-based scenarios present real-world patient presentations, lab findings, and diagnostic challenges, allowing you to apply your knowledge in a practical context.
Start by reviewing cases that cover a range of common infectious diseases, such as pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae or gastroenteritis due to Salmonella. Analyze the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and epidemiological factors to formulate a differential diagnosis.
Then, interpret the laboratory test results, including microscopy, culture, and molecular techniques, to identify the causative pathogen. Consider how the patient’s immune status, comorbidities, and potential exposures may impact the clinical presentation and management.
Explore the rationale for empiric versus targeted antimicrobial therapy, taking into account resistance patterns and adverse effects. Additionally, delve into cases involving emerging or atypical infections, such as Zika virus or Legionella pneumonia, to sharpen your critical thinking skills.
As you work through these case studies, practice communicating your clinical reasoning and management plan, as you would with a supervising physician. By regularly engaging with a diverse range of microbiology case studies, you can develop the analytical skills and clinical acumen essential for success on the USMLE Step 1 exam and beyond.
Incorporating Visual Aids and Mnemonics in Microbiology Study
- Create clear diagrams and flowcharts to illustrate key concepts (e.g., bacterial cell structures, viral replication cycles)
- Develop mnemonics to remember important information (e.g., “ESKAPE” for antibiotic-resistant bacteria)
- Incorporate color-coding, labeling, and visual cues to make study materials more engaging and intuitive
- Practice retrieving information from visual aids and mnemonics to solidify your knowledge
- Utilize active learning strategies to enhance conceptual understanding and improve recall
- Incorporate visual aids and mnemonics into your regular microbiology study routine to better prepare for the USMLE Step 1 exam
Understanding Fungal Pathogenesis and Host Immune Responses
Fungal infections pose a significant challenge in clinical practice, particularly in immunocompromised patients.
On the other side of the host-pathogen interaction, explore the complex interplay between fungi and the innate and adaptive immune responses.
Examine the key pattern recognition receptors, such as Toll-like receptors and C-type lectin receptors, that detect fungal molecular patterns and trigger inflammatory cascades.
Understand how phagocytic cells, including neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells, recognize, engulf, and attempt to eliminate fungal pathogens.
Delve into the role of cytokines, chemokines, and other immune effectors in coordinating the antifungal immune response.
Explore how T cell-mediated and humoral immunity contribute to protection against fungal infections, as well as the implications of immunodeficiencies in predisposing individuals to invasive mycoses.
By integrating this comprehensive knowledge of fungal virulence mechanisms and host immune defenses, you can develop a robust understanding of fungal pathogenesis that will be invaluable for the USMLE Step 1 exam.
Diagnostic Tests in Microbiology: Interpretation and Limitations
Diagnostic tests play a vital role in identifying and characterizing microbial pathogens. This section will discuss various diagnostic tests used in clinical microbiology, including microscopy, culture, serology, and molecular techniques. It will also address the interpretation of test results and the limitations of each method.
Microbiology and Public Health: Preventing Fungal Outbreaks
Microbiology has a significant impact on public health, as it helps in the prevention and control of infectious diseases. This section will explore the role of microbiology in public health, with a specific focus on preventing fungal outbreaks. It will highlight strategies for surveillance, infection control, and public awareness campaigns to mitigate the spread of fungal infections.
Integrating Microbiology with Other Medical Disciplines
Microbiology is the foundation that underpins so many other areas of medicine, and savvy students know that integrating this critical field with other disciplines is key to success.
Take for example the work being done at Mayo Clinic – their interdisciplinary approach brings together microbiologists, immunologists, and clinicians to tackle complex infectious diseases.
Or consider the partnership between Merck and the CDC, where they’re leveraging microbiology insights to develop next-gen vaccines.
Even in digital health, companies like Babylon Health are using machine learning to marry microbiology data with symptom tracking, allowing for faster, more accurate diagnoses.
The takeaway? Mastering microbiology is just the start – the real magic happens when you start connecting the dots across specialties.
That’s why resources like Sketchy Micro are so valuable, equipping you with the microbiology foundation to thrive in any medical setting.
With the right interdisciplinary mindset, the possibilities are endless!
Microbiology Research and Emerging Trends
Explore the frontiers of microbial genomics and metagenomics, and their impact on understanding the human microbiome
- Delve into the rapidly advancing field of molecular diagnostics, including next-generation sequencing and multiplex PCR
- Examine how the growing knowledge of microbial pathogenesis is driving the development of novel antimicrobial agents, such as biologics, phage therapies, and targeted inhibitors
- Investigate the burgeoning area of host-directed therapies and their potential implications for personalized medicine
- Stay vigilant regarding the emergence of zoonotic diseases and antimicrobial resistance, two critical global health challenges
- Cultivate a comprehensive understanding of cutting-edge microbiology research and its clinical applications
- Position yourself at the forefront of this dynamic and rapidly evolving field
- Equip yourself with the knowledge and critical thinking skills necessary to excel on the USMLE Step 1 exam and beyond
Microbiology Practice Questions and Exam Preparation Tips
Acing your microbiology exams takes more than just memorizing textbook facts – it’s all about building that critical thinking muscle.
The best way to do that? Diving into practice questions, my friends.
Sites like Lecturio and UWorld are microbiology question goldmines, with thousands of high-yield practice problems to put your knowledge to the test.
And don’t forget about good old Anki – creating flashcards and doing spaced repetition is a game-changer for cementing those microbe identification skills.
Of course, no microbiology exam prep is complete without a healthy dose of Sketchy Micro. Those incredibly detailed, visual mnemonics will have you remembering bacterial morphologies and virulence factors like a pro.
But it’s not just about the practice questions themselves – make sure you’re also reviewing your incorrect answers carefully to understand where you’re going wrong.
With this well-rounded approach, you’ll be walking into that exam room with the confidence of a seasoned microbiologist.
So get to practicing, future doc – your microbiology success awaits!
Incorporating Evidence-Based Practice in Microbiology
critically evaluate the scientific literature, scrutinizing the methodology, study design, and statistical analysis
- Assess the clinical relevance and generalizability of research findings, considering patient populations and evolving resistance patterns
- Integrate evidence-based knowledge with your understanding of microbial pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics
- Refer to current practice guidelines that incorporate the latest epidemiological data and resistance profiles
- Apply evidence-based reasoning in interpreting lab results, evaluating infection control measures, and predicting pathogen emergence
- Cultivate a mindset of evidence-based practice to ensure your clinical decision-making is grounded in the most up-to-date and scientifically sound microbiology knowledge
- Prepare for success on the USMLE Step 1 exam and beyond by incorporating evidence-based practice in microbiology
Cultivating a Passion for Microbiology as a Medical Student
As a future doc, it’s easy to get caught up in the glitz and glamour of surgery or the thrill of the ER.
But don’t let those more high-profile specialties blind you to the pure magic of microbiology. This foundational field is the unsung hero of medicine, and developing a genuine passion for it can take your career to new heights.
Just ask the team at the American Society for Microbiology – they’ve seen firsthand how students who immerse themselves in microbiology research and extracurriculars end up as the MVPs of their med school classes.
And speaking of immersion, have you checked out Sketchy Micro yet? Those out-of-this-world animated videos will have you falling head-over-heels for everything from bacterial cell walls to viral life cycles.
Pair that with hands-on lab work and you’re well on your way to becoming a microbiology maven. Trust me, your future patients will thank you.
After all, who do you think is going to be the one solving those puzzling infectious disease cases? The future is in your microbe-loving hands, my friend.
So embrace your inner microbiologist and watch your passion – and career – skyrocket.
FAQ
Q: Are there any other study guides available for medical students?
A: Yes, there are several study guides available for different subjects. You can find a comprehensive biochemistry study guide here, a list of the best USMLE tutors here, and a list of the best anatomy resources here.
Q: Are there any anatomy worksheets available for medical students?
A: Yes, you can find anatomy worksheets in PDF format here. Additionally, you may find cross-sectional anatomy resources here and a comprehensive anatomy study guide here.
Q: How can international medical graduates apply for electives?
A: Applying for electives as an international medical graduate can be challenging. You can find a simple guide to applying for electives here. Additionally, you may find a comprehensive guide on USCE for IMGs here.
Q: What are the best shoes for clinical rotations?
A: Finding suitable shoes for clinical rotations is important for comfort and support. You can find a list of the best shoes for clinical rotations here.
Q: How can medical students make money online?
A: There are various ways for medical students to make money online. You can find information on how to make money online as a medical student here.
Q: Are there any other useful resources for medical students?
A: Yes, you may find the conclusion of Reddit medical school Anki posts here. These resources can provide additional support and guidance for medical students.
For more information on microbiology, you can visit the following links: